Sensitivity to Neutralizing Antibodies and Resistance to Type I Interferons in SARS-CoV-2 R.1 Lineage Variants, Canada
Rajesh Abraham Jacob, Ali Zhang
1, Hannah O. Ajoge
1, Michael R. D'Agostino
1, Kuganya Nirmalarajah, Altynay Shigayeva, Wael L. Demian, Sheridan J.C. Baker, Hooman Derakhshani, Laura Rossi, Jalees A. Nasir, Emily M. Panousis, Ahmed N. Draia, Christie Vermeiren, Jodi Gilchrist, Nicole Smieja, David Bulir, Marek Smieja, Michael G. Surette, Andrew G. McArthur, Allison J. McGeer, Samira Mubareka, Arinjay Banerjee, Matthew S. Miller, and Karen Mossman
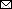
Author affiliations: McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada (R.A. Jacob, A. Zhang, H.O. Ajoge, M.R. D'Agostino, W.L. Demian, S.J.C. Baker, L. Rossi, J.A. Nasir, E.M. Panousis, A.N. Draia, D. Bulir, M. Smieja, M.G. Surette, A.G. McArthur, M.S. Miller, K. Mossman); Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (K. Nirmalarajah, S. Mubareka); University of Toronto, Toronto (A. Shigayeva, C. Vermeiren, A.J. McGeer, S. Mubareka, A. Banerjee); University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada (H. Derakhshani); Research Institute of St. Joe’s Hamilton, Hamilton (J. Gilchrist, N. Smieja, D. Bulir); Vaccine and Infectious Disease Organization, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada (A. Banerjee); University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon (A. Banerjee); University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada (A. Banerjee); University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada (A. Banerjee)
Main Article
Figure 2

Figure 2. Antibody detection in study of sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies and resistance to type I interferons in SARS-CoV-2 R.1 lineage variants, Canada. A, B) S1 (A) and RBD (b) binding IgG determined by using a sandwich ELISA format. Dashed line indicates the limit of detection. C, D) Correlation between S1 and RBD binding IgG for wave 1 (C) and wave 3 (D). E–G) ID50 titers for SB3 (E), R.1 645 (F), and B.1.351 (Beta) VoC (E). Error bars in panels A, B and E–G indicate SD. Statistical significance was calculated by using an unpaired t test for panels A and B and by using 1-way analysis of variance with Tukey multiple comparisons test for panels E–G. ID50, 50% inhibitory dilution; PFU, plaque-forming units; RBD, receptor-binding domain; S1, spike.
Main Article
Page created: May 08, 2023
Page updated: June 20, 2023
Page reviewed: June 20, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
